Radioactive 'snowflakes' act like the tiniest nuclear bombs in the universe
By Mara Johnson-Groh - Live Science Contributor 4 hours ago
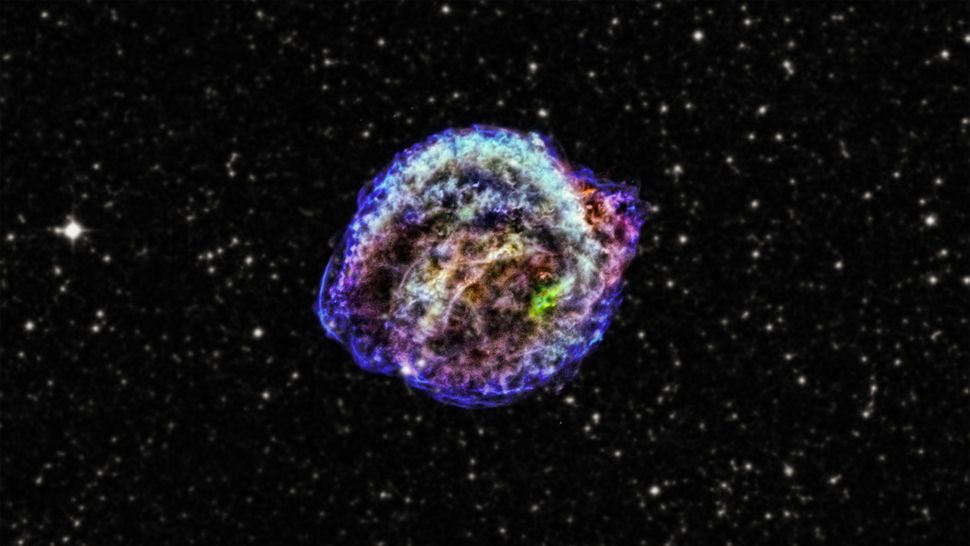
This Chandra X-ray Observatory image shows the remnant of Kepler's supernova, the famous Type 1a supernova explosion that was discovered by Johannes Kepler in 1604. (Image credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/NCSU/M.Burkey et al; Optical: DSS)
Tiny snowflakes of radioactive uranium that trigger massive nuclear blasts might explain some of the universe's more mysterious star explosions.
As smallish stars die, they cool into husks of their former selves known as white dwarfs. New research proposes that atoms of uranium sink to the centers of these aging white dwarf stars as they cool, freezing into snowflake-like crystals no bigger than grains of sand. There, these "snowflakes" can act as some of the tiniest nuclear bombs in the universe, becoming the "spark that sets off the powder keg," said study co-author Matt Caplan, a theoretical physicist at Illinois State University.
"It's important to understand how these explosions occur for all sorts of applications, from the production of elements to the expansion of the universe," Caplan told Live Science.
These unusually dim star explosions are part of a class known as Type Ia supernovas. Typically, scientists think these explosions occur when a white dwarf star reaches a critical mass after siphoning gas from a companion star the white dwarf is in orbit with. Because Type Ia supernovas explode when they reach the same mass, they have the same brightness. This uniform brightness allows them to be used as a standard by which t distances in the universe are measured.
More:
https://www.livescience.com/radioactive-snowflakes-trigger-nuclear-blasts.html?utm_source=notification

