General Discussion
In reply to the discussion: Explain to me why I am wrong, please. [View all]Celerity
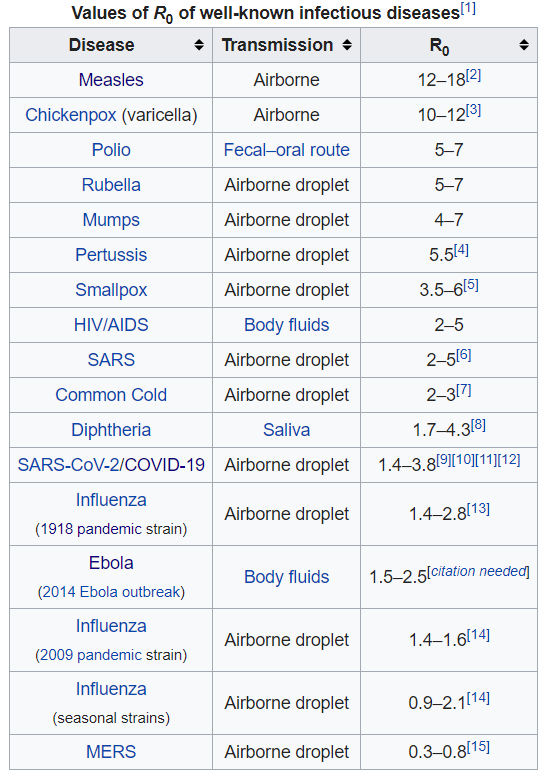
(53,517 posts)HYPOTHETICAL viral penetration rate, and the largest was what you have to get to (in the absence of a vaccine) to achieve herd immunity given the 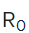 value of the virus at 3.0. I used those to show the absurdity of a 40% lethality rate, as many contagious diseases get to those larger levels of populace infection rates. I NEVER SAID that the penetration rate for COVID-19 was anywhere NEAR THOSE LARGE numbers at the present time, but it most definitely could get up there if we massively fail at mitigation, and/or a 2nd, or even 3rd wave rolls through. The higher the
value of the virus at 3.0. I used those to show the absurdity of a 40% lethality rate, as many contagious diseases get to those larger levels of populace infection rates. I NEVER SAID that the penetration rate for COVID-19 was anywhere NEAR THOSE LARGE numbers at the present time, but it most definitely could get up there if we massively fail at mitigation, and/or a 2nd, or even 3rd wave rolls through. The higher the 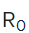 is the greater the percentage of the populace infected needs to be for herd immunity to kick in.
is the greater the percentage of the populace infected needs to be for herd immunity to kick in.
For brevity's sake, I will not even start to get into mutagenic possibilities for the virus.
A contagious disease with an 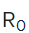 of 2.0 means 50% or so of the populace needs to be infected in order for herd immunity to kick in. An
of 2.0 means 50% or so of the populace needs to be infected in order for herd immunity to kick in. An 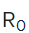 of 2.5 means around 60% need to be infected, and an
of 2.5 means around 60% need to be infected, and an 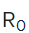 of 3.0 means 66.7% of the populace needs to be infected in order for herd immunity to kick in. COVID-19 has been postulated to have an
of 3.0 means 66.7% of the populace needs to be infected in order for herd immunity to kick in. COVID-19 has been postulated to have an 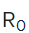 of between 2.0 and 3.5. It is basic science that I was using.
of between 2.0 and 3.5. It is basic science that I was using.
I will add one thing, and I have doubts over this, BUT I have seen a couple epidemiologists on MSNBC who are now saying that they think COVID-19 has an 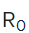 of 6 or so. If that is the case, we are well and truly fucked until a vaccine comes around.
of 6 or so. If that is the case, we are well and truly fucked until a vaccine comes around.
The 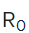 (R-naught) value is how contagious a disease-causing pathogen is.
(R-naught) value is how contagious a disease-causing pathogen is.

https://www.healthline.com/health/r-nought-reproduction-number
Understanding the possibilities
R0 is pronounced “R naught.” It’s a mathematical term that indicates how contagious an infectious disease is. It’s also referred to as the reproduction number. As an infection spreads to new people, it reproduces itself.
R0 tells you the average number of people who will catch a disease from one contagious person. It specifically applies to a population of people who were previously free of infection and haven’t been vaccinated. If a disease has an R0 of 18, a person who has the disease will transmit it to an average of 18 other people, as long as no one has been vaccinated against it or is already immune to it in their community.
What do R0 values mean?
Three possibilities exist for the potential spread or decline of a disease, depending on its R0 value:
If R0 is less than 1, each existing infection causes less than one new infection. In this case, the disease will decline and eventually die out.
If R0 equals 1, each existing infection causes one new infection. The disease will stay alive and stable, but there won’t be an outbreak or an epidemic.
If R0 is more than 1, each existing infection causes more than one new infection. The disease will spread between people, and there may be an outbreak or epidemic.
snip